
Including headers, footers, page numbers, margins and columns Version numbers as a part of the link, the structure of sections Note: Although many of the links below contain certain Troubleshoot Sections, Headers, Footers, Page Numbers & Set Page Borders for a document or a particular sectionīe able to see on screen or in your document Orientation changes from Portrait to Landscape and backĪdd Your Custom Watermarks to the Galleryįirst page of a multi-page document (or only on Only on the last page or some other page without aĪ Particular Section or With Multiple Sections
for mirrored headers/footers - two-sided printing) Use advanced formatting in Headers and Footers What You Will LearnĪfter completing this lesson, you will be able to: Problems or questions with one of these, you need to know moreĪbout Sections in Word. (portrait/landscape), margins and columns. Sections are the Word feature that controls page numberįormatting, headers and footers, orientation Sections, Section Breaks, and Headers and Footers in Microsoft Word The View tab has five groups of related commands Document Views, Show/Hide, Zoom, Window and Macros.Sections / Headers and Footers in Microsoft Word - a Tutorial in the Intermediate Users Guide to Microsoft Word (supplemented Legal Users' Guide to Microsoft Word) Its primary purpose is to offers you different ways to view your document. It also enables you to control various layout tools like boundaries, guides, rulers. This tab allows you to switch between Single Page and Two Page views. The View tab is located next to the Review tab. The Review tab has six groups of related commands Proofing, Comments, Tracking, Changes, Compare and Protect. It helps you proofread your content, to add or remove comments, track changes, etc. This tab offers you some important commands to modify your document. The Mailings tab has five groups of related commands Create, Start Mail Merge, Write & Insert Fields, Preview Results and Finish.
WORD 2016 HEADER AND FOOTER DESIGN TOOL BAR PDF
It allows you merge emails, writing and inserting different fields, preview results and convert a file into a PDF format. It is the least-often used tab of all the tabs available in the Ribbon. The References tab has six groups of related commands Table of Contents, Footnotes, Citations & Bibliography, Captions, Index and Table of Authorities. It also offers commands to create a table of contents, an index, table of contents and table of authorities.
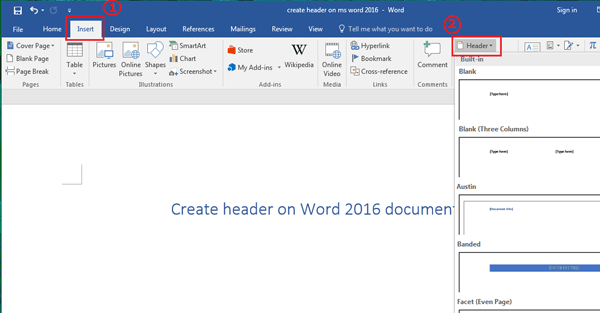
It allows you to enter document sources, citations, bibliography commands, etc. The Page Layout tab has five groups of related commands Themes, Page Setup, Page Background, Paragraph and Arrange. you can change the page size, margins, line spacing, indentation, documentation orientation, etc. This tab allows you to control the look and feel of your document, i.e. The Insert tab has seven groups of related commands Pages, Tables, Illustrations, Links, Header & Footer, Text and Symbols. It is commonly used to add tables, pictures, clip art, shapes, page number, etc. As the name suggests, it is used to insert or add extra features in your document. Insert Tab is the second tab in the Ribbon. It also helps you to return to the home section of the document. It helps you change document settings like font size, adding bullets, adjusting styles and many other common features. It has five groups of related commands Clipboard, Font, Paragraph, Styles and Editing. The Home tab is the default tab in Microsoft Word. It gives you quick access to the commonly used commands that you need to complete a task. Each tab has specific groups of related commands. It comprises seven tabs Home, Insert, Page layout, References, Mailing, Review and View. It is located below the Quick Access Toolbar and the Title Bar. The Ribbon is a user interface element which was introduced by Microsoft in Microsoft Office 2007.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
